As an engineer at SuperPCBA, I am pleased to introduce this article about Flex PCB Coverlay. In modern electronic design, flexible PCBs are widely used in various advanced electronic products due to their lightweight, flexibility, and efficiency. The flexible coverlay, as a critical component, plays an essential role in providing protection and insulation. In this article, we will explore the definition, significance, classification, and differences between coverlay and solder mask. Through detailed explanations of these key points, we hope to help you understand and utilize this important material more comprehensively.
Overview of Flex PCB Coverlay

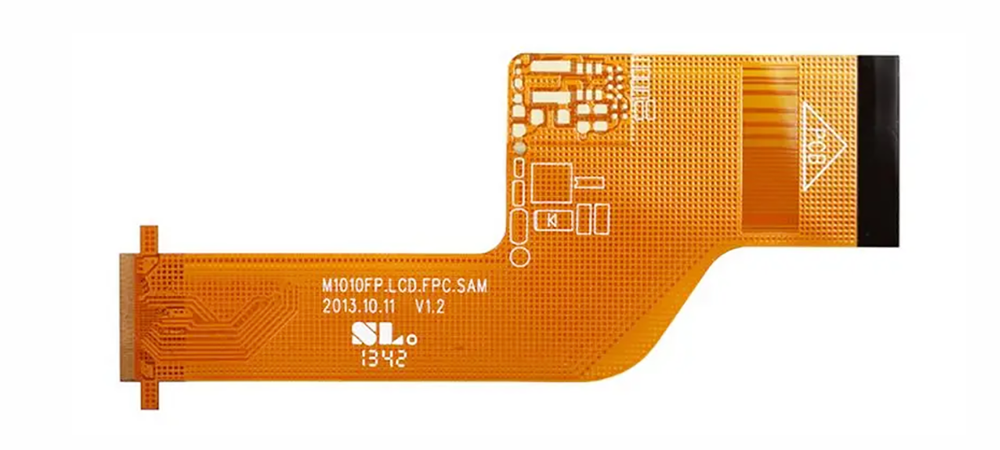
Flex PCB coverlay is typically made from polyimide material with a pre-coated adhesive. During the manufacturing process, the coverlay is thermally bonded to the flexible PCB to ensure its durability and reliability. It primarily covers and protects the exposed copper traces on the flexible PCB, providing electrical insulation, mechanical protection, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and dust. This coverlay is widely used in electronic products that require high flexibility, such as mobile phones, wearable devices, and medical equipment.
Importance of Using Flex PCB Coverlay
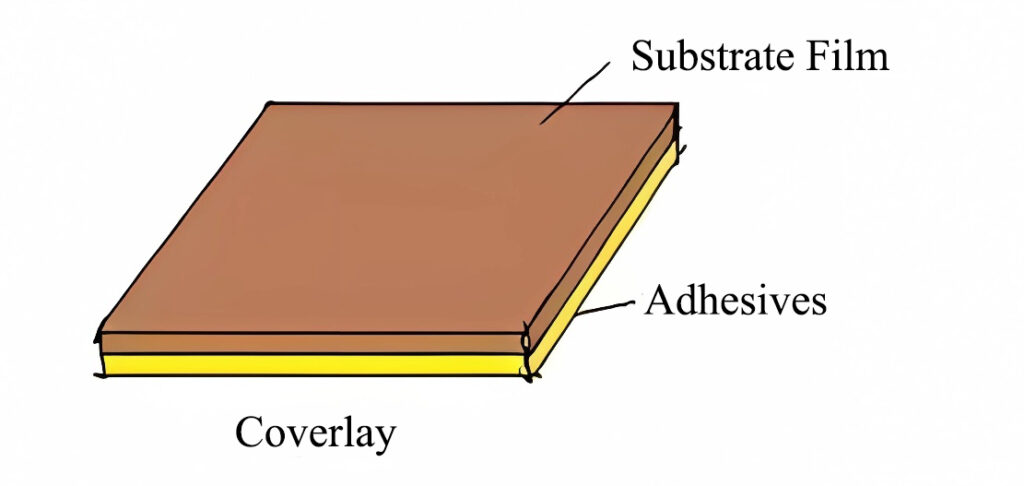
Most flexible PCBs use a coverlay due to the essential mechanical protection and electrical insulation it provides, enhancing the board’s environmental adaptability and long-term stability.
Specific benefits include:
- Mechanical Protection: The coverlay shields the copper traces on the flexible PCB from mechanical damage like scratches, bends, and wear, extending the PCB’s lifespan.
- Environmental Protection: It offers moisture, dust, and chemical resistance, ensuring the PCB’s stability and reliability under various environmental conditions.
- Electrical Performance:
- Electrical Insulation: The coverlay provides effective electrical insulation, preventing short circuits between different circuits.
- Stability: It prevents the oxidation and degradation of copper traces, maintaining the electrical performance of the PCB over long-term use.
- Manufacturing and Application Needs:
- Complex Design: As electronic product designs become more complex, flexible PCBs need to achieve multilayer interconnections and high-density wiring in small spaces, where the coverlay offers necessary protection and support.
- Wide Applications: From consumer electronics and medical devices to automotive electronics and aerospace, flexible PCBs are widely used in fields requiring high reliability and flexibility, making the coverlay a standard design requirement in these applications.
Thus, the coverlay is essential in the design and manufacturing of most flexible PCBs. Although in some simple applications, a flexible PCB may only require basic electrical connections and conduction functions without additional mechanical protection or electrical insulation, this is usually an exception rather than the norm.
Types of Flex PCB Coverlay
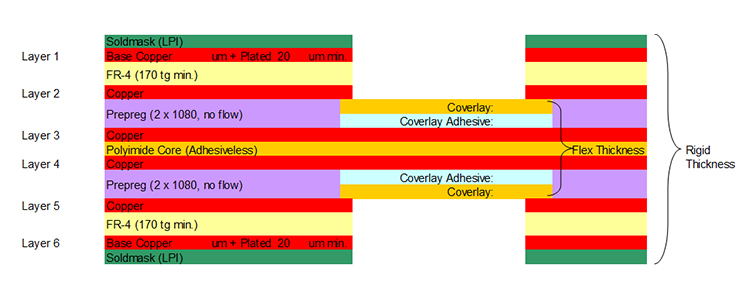
Flex PCB coverlays come in various specifications and classifications based on different materials, thicknesses, uses, and performance characteristics. Common classification methods include:
- Material Type:
- Polyimide: The most common material, known for high-temperature resistance and excellent electrical insulation.
- Polyester: Typically used for low-cost, low-temperature applications.
- Thickness:
- Thin Films (usually 12.5µm to 50µm): Suitable for applications requiring high flexibility.
- Thicker Films (like 75µm or thicker): Provide better mechanical protection and wear resistance but are less flexible.
- Adhesive Type:
- Thermosetting Adhesive: Cures at high temperatures, offering strong adhesion and high-temperature performance.
- Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive (PSA): Bonds through pressure, suitable for low-temperature applications.
- Application Scenarios:
- Single-Sided Coverlay: Covers one side of the PCB, suitable for simple flexible circuits.
- Double-Sided Coverlay: Covers both sides of the PCB, used for complex multilayer flexible PCBs.
- Colors:
- Amber: The natural color of polyimide material.
- Other Colors like Black, White: Used for specific application requirements or appearance needs.
Different specifications and classifications can be selected according to specific application needs to ensure the reliability and performance of the flexible PCB in practical use.
Similarities and Differences Between Flex PCB Coverlay and Solder Mask

While both coverlay and solder mask provide protection and insulation, their materials, application methods, and specific uses differ. Coverlays are more suitable for flexible PCBs, offering higher mechanical protection and flexibility, whereas solder masks are more broadly used for various PCBs to prevent soldering issues and copper trace oxidation.
Specific details include:
- Similarities:
- Protective Function:
- Coverlay: Protects the exposed copper traces on flexible PCBs from physical damage, moisture, and contamination.
- Solder Mask: Protects copper traces on PCBs from oxidation, physical damage, and solder bridging during soldering.
- Electrical Insulation:
- Coverlay: Provides electrical insulation to prevent short circuits between different circuits.
- Solder Mask: Offers electrical insulation to prevent short circuits during soldering.
- Protective Function:
- Differences:
- Materials:
- Coverlay: Typically made from polyimide or polyester, providing high flexibility and heat resistance.
- Solder Mask: Usually made from liquid photosensitive materials (like epoxy resin), which are cured after exposure and development.
- Application Methods:
- Coverlay: Thermally or pressure-bonded to the flexible PCB, adapting to the board’s bending and movement.
- Solder Mask: Coated onto rigid or flexible PCBs through screen printing, spraying, or coating, then cured through exposure, development, and baking.
- Main Uses:
- Coverlay: Mainly used for flexible PCBs, especially in applications requiring frequent bending and movement, providing mechanical protection and insulation.
- Solder Mask: Widely used for rigid and flexible PCBs, primarily to prevent solder bridging and oxidation, keeping the pads clean.
- Materials:
Through this article, we hope you have gained a deeper understanding of the definition, significance, classification, and differences of flex PCB coverlays compared to solder masks. Flex coverlays play a crucial role in protecting PCBs and enhancing performance, making them one of the indispensable materials in modern electronic products. If you have any questions or needs regarding flex PCB coverlays or other electronic manufacturing aspects, we sincerely invite you to contact us at sales@superpcba.com. SuperPCBA is committed to providing you with professional consultation and high-quality electronic manufacturing solutions. We look forward to working with you to advance electronic technology innovation and development. Thank you for reading!



