What is Rigid PCBs?
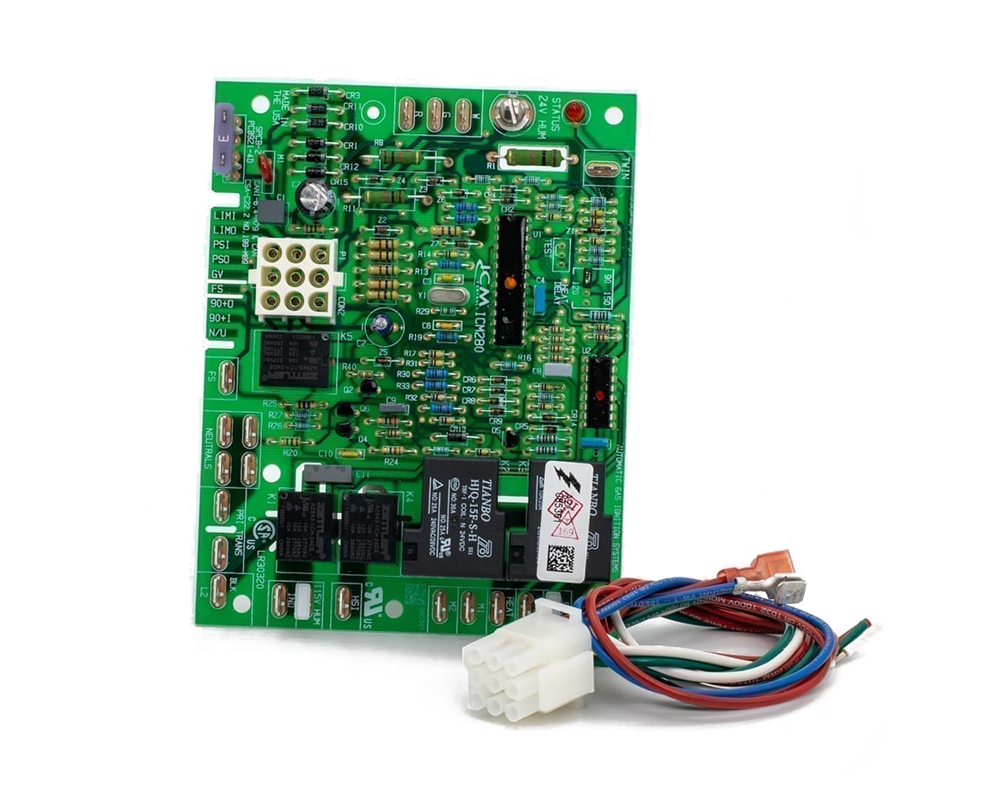

Rigid printed circuit board (PCB) is a commonly used electronic component carrier. It is made of a rigid material, typically glass fiber-reinforced epoxy resin, to provide support and connection for electronic components. Rigid PCBs offer stable structural support and reliable circuit connections, enabling electronic components to function correctly in fixed positions. They often feature high-density routing and complex circuit designs to meet the requirements of sophisticated electronic systems.
What is Flexible PCBs?
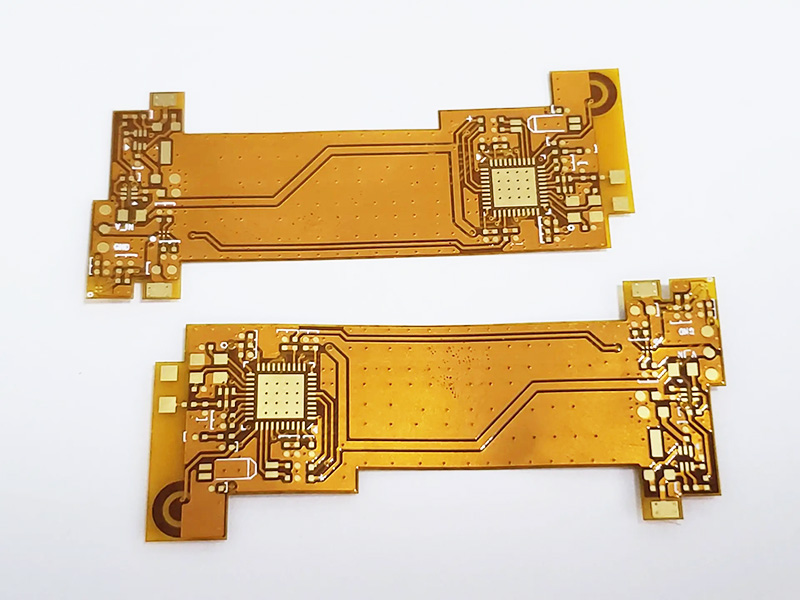
Flexible circuit board, also known as flex PCB, is an electronic component carrier made of flexible substrate material. It possesses the characteristics of being bendable, foldable, and twistable. Flexible circuit boards typically use flexible polymer films as the substrate material, such as polyimide (PI), polyester (PET), and others. They find wide applications in wearable devices, medical equipment, flexible displays, automotive electronics, and more. Flex PCBs provide flexible design options and innovative product solutions.
What is Flex-Rigid PCBs?
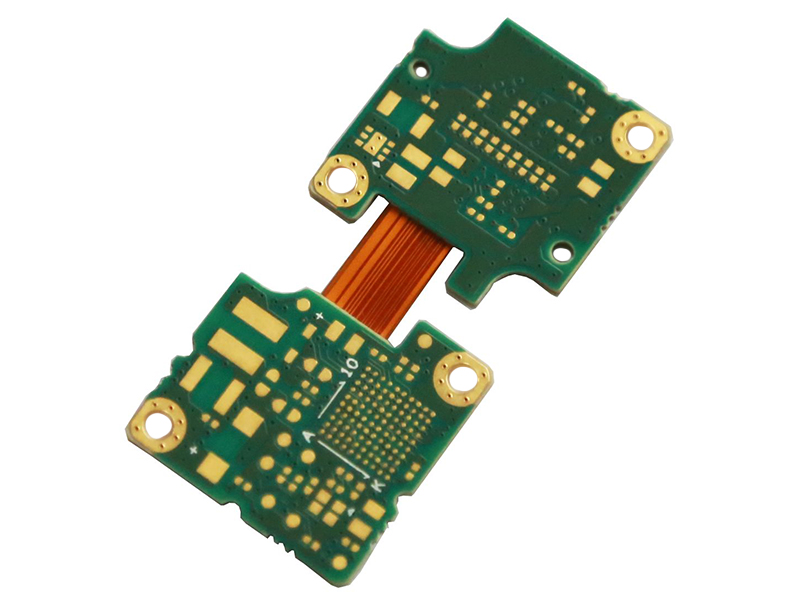
Rigid-flex PCB, a special type of circuit board, combines the characteristics of rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs. It features both rigid and flexible areas, utilizing the connection between the two to achieve circuit functionality. Rigid-flex PCBs are widely used in applications that require both rigid and flexible properties, such as wearable devices, medical equipment, aerospace devices, automotive electronics, and more. They leverage the advantages of both rigid and flexible circuit boards, offering greater design flexibility and reliable circuit interconnect solutions.
Rigid-flex PCBs possess the characteristics of both rigid and flexible areas. In this article, the focus is on analyzing the differences between rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs, followed by an exploration of the characteristics of rigid-flex PCBs.
Macro Differences between Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs:

Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs are two common types of circuit boards that have some differences in terms of structure, characteristics, and applications. Here are a few key points analyzing them from a macro perspective.
- Structure and Materials: Rigid PCB: Typically uses rigid substrate materials such as glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin (FR4). It has a fixed shape and size and cannot be bent or folded. Flexible PCB: Uses flexible substrate materials such as polyimide (PI) or polyamide resin (PAA). It has high flexibility and can be bent, folded, or twisted in three-dimensional space.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Rigid PCB: Suitable for applications that require a fixed shape and stable structure, such as large electronic devices and computer motherboards. Not suitable for applications that require bending or compact spaces. Flexible PCB: Suitable for applications that require bending or folding, such as wearable devices, flexible displays, and foldable smartphones. It can adapt to complex shapes and curved surfaces.
- Layout and Wiring: Rigid PCB: Typically uses straight-line wiring and larger angle corners. The distance between the traces is shorter, making it easier to achieve high-density wiring. Flexible PCB: Can be bent and folded in different planes, allowing traces to be routed along three-dimensional surfaces to accommodate more complex layout requirements.
- Size and Weight: Rigid PCB: Due to the use of thicker substrates and more layers, rigid PCBs are relatively thick and heavy, making them unsuitable for weight-restricted applications. Flexible PCB: Due to the use of flexible thin-film materials, flexible PCBs have smaller dimensions and lighter weight, making them suitable for slim and compact design requirements.
- Cost and Manufacturing Complexity: Rigid PCB: Due to mature manufacturing processes and widespread material usage, rigid PCBs have lower manufacturing costs and are relatively easy to obtain. Flexible PCB: Due to the complexity of the manufacturing process, flexible PCBs have relatively higher manufacturing costs.
Micro Differences between Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs:

Here are a few points analyzing the differences between rigid boards and flexible boards from a micro perspective:
- Bend Radius: Rigid boards typically require larger bend radii, usually in the range of tens of millimeters, to prevent circuitry breakage or damage. Flexible boards can accommodate smaller bend radii, typically within a few millimeters, due to their higher flexibility.
- Line Width and Spacing: Rigid boards can achieve smaller line widths and spacings, often reaching a few tens of micrometers, to meet the demands of high-density routing and miniaturization. Flexible boards have relatively larger minimum line widths and spacings, typically in the range of a few hundred micrometers, due to the flexibility of the materials.
- Number of Layers and Stacking: Rigid boards usually have a higher number of layers, reaching dozens or more, to enable complex circuit functionality and signal separation. Flexible boards, due to the limitations of flexible materials, are generally more challenging to achieve multi-layer stacking and are commonly single-sided or double-sided structures.
- Environmental Adaptability: Rigid boards are suitable for relatively stable environments and have weaker adaptability to temperature variations and vibrations. Flexible boards, with their flexibility and ability to withstand bending, are suitable for applications requiring adaptation to temperature changes and vibrations.
- Cost Comparison: Rigid boards have lower manufacturing costs due to mature manufacturing processes and the availability of widely used materials. Flexible boards have relatively higher manufacturing costs due to the complexity of manufacturing processes and the need for specialized substrate materials.
Of course, these data and analyses represent general comparisons, and actual figures may vary depending on manufacturers, specifications, and specific requirements. During the specific design and manufacturing process, evaluation and selection should be based on specific requirements.
Application Differences between Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs:
In terms of practical applications, rigid circuit boards and flexible circuit boards have some differences in their respective fields. Here are the main differences in their application domains:
Applications of Rigid Circuit Boards:
- Electronic Devices: Rigid circuit boards are widely used in electronic devices such as computer motherboards, mobile phones, televisions, and audio systems.
- Communication Equipment: Rigid circuit boards are extensively utilized in the field of communication equipment, including routers, switches, and base stations.
- Industrial Control Systems: Rigid circuit boards play a crucial role in industrial control systems used for controlling and monitoring various industrial equipment and processes.
- Automotive Electronics: Rigid circuit boards are also commonly employed in automotive electronics for controlling the vehicle’s electronic systems, dashboards, navigation systems, etc.
Applications of Flexible Circuit Boards:
- Wearable Devices: Flexible circuit boards find extensive applications in wearable devices such as smart wristbands, smartwatches, health monitors, etc.
- Flexible Displays: Flexible circuit boards have significant applications in the field of flexible displays.
- Medical Devices: Flexible circuit boards are widely used in medical devices, including medical monitors and implantable medical instruments.
- Aerospace Industry: Flexible circuit boards are also utilized in the aerospace industry for applications such as aerospace instruments and devices.
Please note that the above-mentioned applications are common examples, and the actual usage of rigid and flexible circuit boards may vary depending on manufacturers, specifications, and specific requirements. During the design and manufacturing process, it is essential to evaluate and select the appropriate board type based on specific needs.
The Characters of Flex-Rigid PCBs
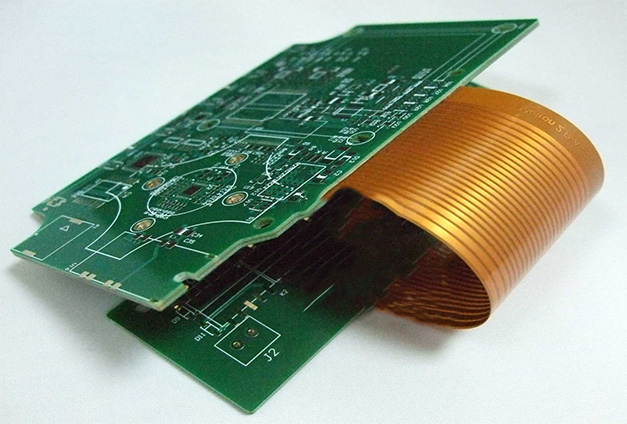
The circuit board that combines rigidity and flexibility, also known as a rigid-flex circuit board or hybrid circuit board, possesses the following notable characteristics:
- Structural Versatility: The rigid-flex circuit board integrates rigid and flexible regions on the same board, allowing it to adapt to various shapes, space limitations, and installation requirements.
- Flexibility and Bendability: The flexible regions of the rigid-flex circuit board can be bent, folded, or flexed, enabling it to accommodate complex surfaces, bends, or layouts in three-dimensional space.
- High-Density Wiring: The rigid-flex circuit board achieves high-density wiring in the rigid regions to meet the demands of intricate circuit designs and signal transmission. Simultaneously, the flexible regions enable free-form wiring, adapting to different shapes and layout requirements.
- Mechanical Stability: By combining rigid and flexible regions, the rigid-flex circuit board attains mechanical stability. The rigid regions provide structural support and stability, while the flexible regions accommodate mechanical deformation and vibration.
- Multifunctionality: The flexible regions of the rigid-flex circuit board can be utilized for integrating additional components or sensors, facilitating multifunctional designs. For instance, in wearable devices, the flexible regions can accommodate sensors, touch buttons, or flexible displays.
- Reliability and Durability: The design of rigid-flex circuit boards considers the connectivity and interfaces between the rigid and flexible regions to ensure reliable electrical connections and long-term durability.
In summary, the rigid-flex circuit board leverages the advantages of both rigid and flexible circuit boards while overcoming their respective limitations, providing greater design flexibility and application versatility. This has led to wide-ranging applications of rigid-flex circuit boards in fields such as wearable devices, flexible displays, medical equipment, and aerospace industries.
Do you now understand the differences and characteristics of flexible circuit boards and rigid-flex boards? Therefore, it is important to choose different circuit boards based on the specific features and requirements of your product. It is not always the case that flexible boards are better than rigid-flex boards, and rigid-flex boards are not suitable for all products. Sometimes, even if a product is best suited for a flexible board, considering the specific market conditions and cost control requirements, it may still be necessary to use a rigid board or a rigid-flex board.
At SuperPCBA, we have over a decade of experience in design and production, and we can provide mature product design solutions based on the requirements of our customers. We are here to help our customers solve product issues. We always prioritize our customers, align with market trends, and provide excellent customer service and support. Whether you are a new or existing customer, please feel free to contact us for consultation and negotiation.



