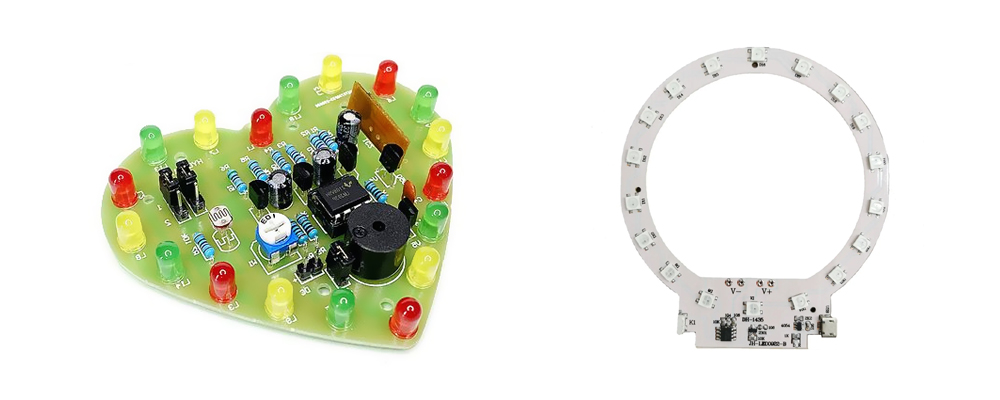
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes), as efficient and long-lasting lighting components, play a crucial role in modern electronic devices and the lighting industry. Today, let’s explore the classification of LEDs in circuit board production applications. Through this article, we aim to assist you in better understanding and applying LED technology, thus enhancing the performance and effectiveness of your projects and products.
LED Overview
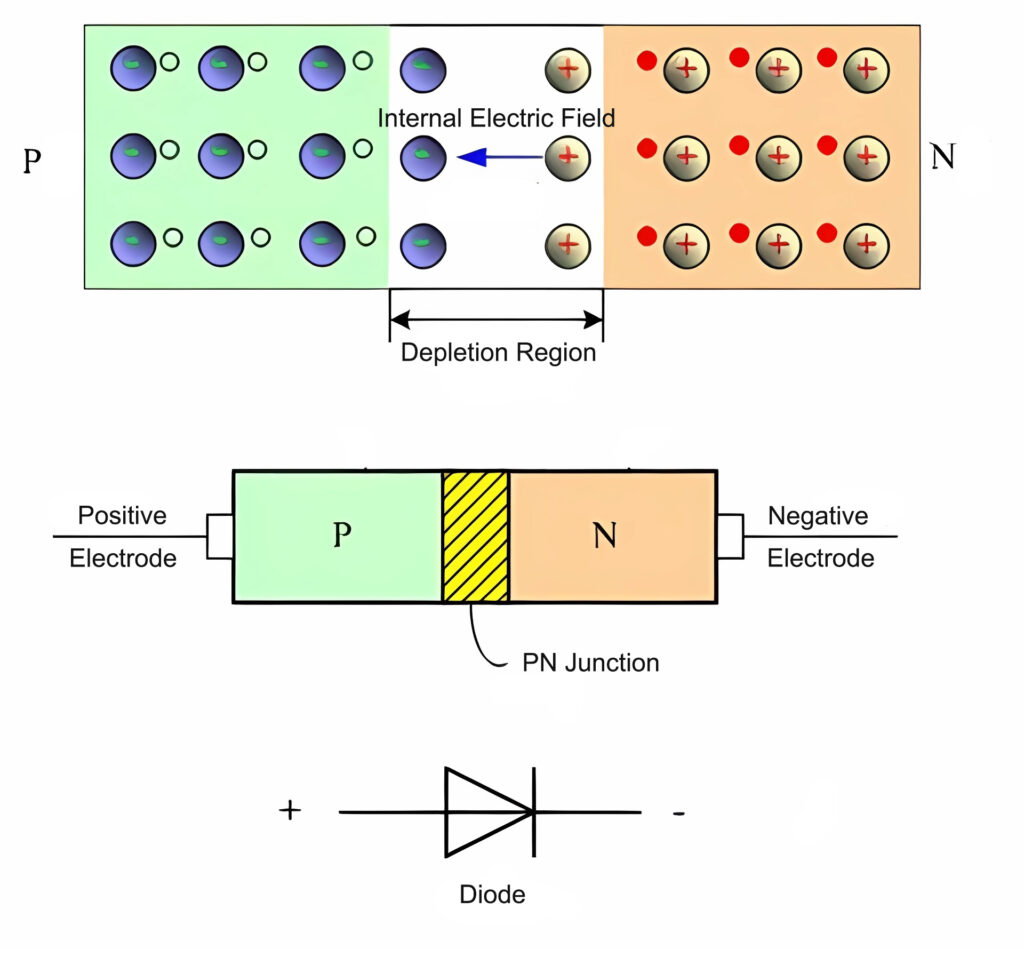
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are light sources that utilize semiconductor devices to emit light. They possess characteristics such as high efficiency, energy efficiency, long lifespan, resistance to shock and vibration, and compact size, making them widely utilized in the fields of illumination and display.
Structure of LED: The semiconductor chip of an LED consists of two parts – one part being the P-type semiconductor where holes dominate, and the other end being the N-type semiconductor where electrons are prevalent. When these two semiconductors are connected, they form a P-N junction.
Working principle of LED: When current flows through the semiconductor chip of an LED via a conductor, electrons are pushed into the P-region. Within the P-region, electrons combine with holes, emitting energy in the form of photons, which is the principle behind LED light emission. The wavelength of light, and thus its color, is determined by the materials forming the P-N junction.
LEDs can emit light directly in red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, orange, purple, and white colors.
Classification of LEDs
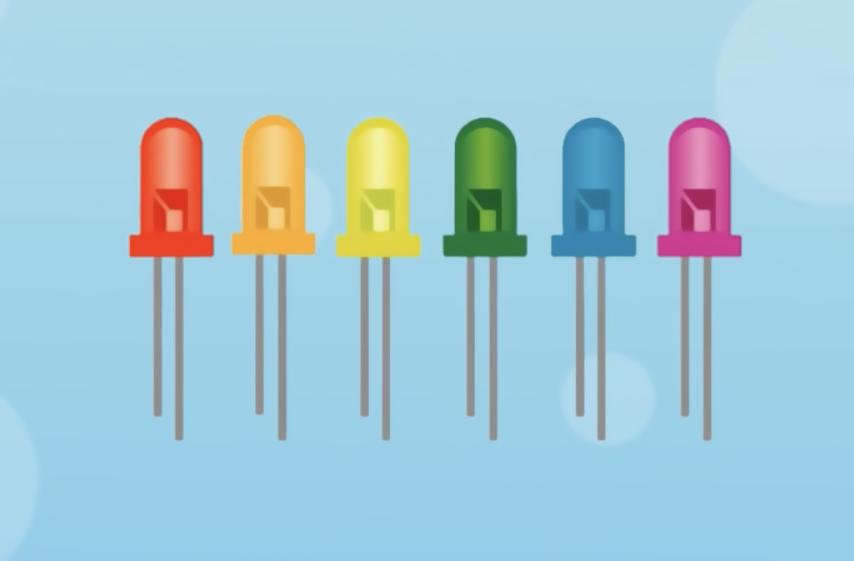

LEDs can be classified according to various principles, including their light emission principles, colors, power ratings, applications, size and shape, operating voltages, and more. However, from the perspective of circuit board assembly and component integration, we primarily classify LEDs based on their packaging methods and signal reception modes, as detailed below.
Packaging Forms: LEDs can be classified into various types based on their different packaging methods, including surface-mount type, through-hole type, chip-on-board type, and encapsulated type.
Signal Reception: LEDs can be categorized into addressable LEDs and wireless LEDs based on their signal reception modes.
LED Packaging Forms
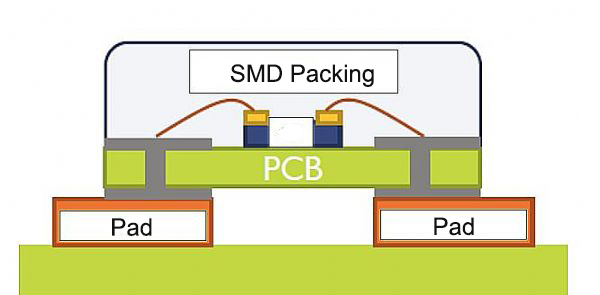
DIP LED and SMD LED are two common packaging forms of LEDs, representing different packaging types:
DIP LED (Dual in-line Package LED): DIP LED is a traditional LED packaging form, similar to the conventional dual in-line packaging. The LED chip is connected to the circuit board via two metal leads. DIP LEDs typically have larger dimensions and packaging volumes, suitable for applications with less stringent size requirements, such as indicator lights, displays, etc.
SMD LED (Surface-mount Device LED): SMD LED is a surface-mount type LED, suitable for surface-mount technology (SMT). The LED chip is directly soldered onto the surface of the circuit board without the need for lead connections. SMD LEDs have smaller dimensions and packaging volumes, suitable for applications with stricter size requirements, such as backlighting, automotive lighting, displays, etc.
In summary, DIP LED and SMD LED are two common packaging forms of LEDs, each with its own characteristics and suitable applications. DIP LED is suitable for applications with less stringent size requirements, while SMD LED is suitable for applications with stricter size requirements and has better applicability in SMT processes.
Signal Reception

Addressable LED
Addressable LEDs can be controlled individually or in groups, which is why they are called “addressable.” They allow you to create dynamic lighting effects simultaneously on different parts of the LED strip or at customizable intervals, offering a wide range of creative possibilities. Each LED has a built-in controller that communicates through a digital protocol, allowing data to pass from one LED to the next in a serial daisy-chain. This enables a microcontroller or LED controller to send precise instructions for individual colors and brightness. This level of control contrasts with common RGB strips with a single control chip, offering enhanced flexibility and creative potential.
Wireless LED
If LEDs could light up without any wires or soldering, it sounds really interesting, right? That’s what wireless LEDs or inductive LEDs can achieve. Inductive coupling is the most common type of wireless power transmission for LED lights. It works by using two coils of wire to create a magnetic field. When the two coils are close together, the magnetic field induces a current in the receiver coil. This current can then be used to power the LED lights. The possibilities with these special wireless LEDs are virtually limitless. Imagine using them for a whimsical and eye-catching cosplay outfit, or employ them for stunning and versatile lighting decoration in your home.
Conclusion
Through this article, we hope you have gained a deeper understanding of the key elements in high-speed PCB design and can apply this knowledge in your practical projects. If you have any questions or collaboration needs in high-speed PCB design or other electronic manufacturing aspects, we sincerely invite you to contact us at sales@superpcba.com. SuperPCBA is committed to providing you with professional consulting services and high-quality electronic manufacturing solutions. Let’s work together to advance your electronic products!
Thank you for reading!



