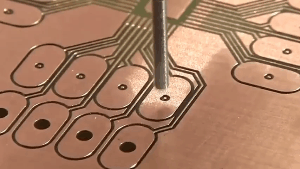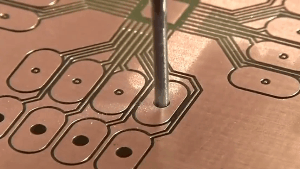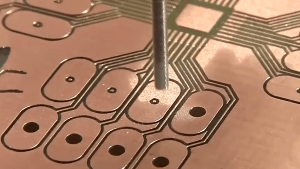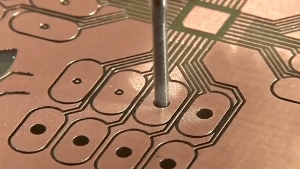
Double-sided PCB, also known as double-layer PCB, is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces and components on both sides of the board. These copper traces and components are connected through holes drilled in the board called vias. The vias allow for the electrical connections between the two layers of copper traces, making it possible to design more complex circuits with higher density than single-sided PCBs. Double-sided PCBs are commonly used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, telecommunications, medical equipment, and industrial control systems.

The main difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs is the number of copper layers on the board, which affects the complexity and density of the design as well as the cost of manufacturing.


Higher density: Double-sided PCBs offer more space for components and copper traces, allowing for higher density designs with more components per unit area.
Improved performance: Double-sided PCBs can be designed to reduce signal interference and improve signal integrity, resulting in better overall performance.
More complex designs: The ability to use both sides of the board allows for more complex and sophisticated designs with multiple layers of copper traces.
Smaller form factor: The ability to place components on both sides of the board allows for a smaller overall form factor of the PCB.
More expensive: Double-sided PCBs are more expensive to manufacture than single-sided PCBs due to the need for vias and other additional manufacturing steps.
Versatile applications: Double-sided PCBs are used in a wide range of applications, from simple consumer electronics to high-performance industrial control systems.
Better thermal dissipation: The additional layer of copper traces allows for better heat dissipation, making double-sided PCBs a good choice for high-power applications.
Overall, double-sided PCBs offer greater flexibility, better performance, and more design options than single-sided PCBs, although they are generally more expensive to manufacture.S
Double or multiple layers of traces on a single layer PCB often require the use of vias to establish connections. Copper on the walls of the vias serves as a conduit between the copper traces on the upper and lower layers.
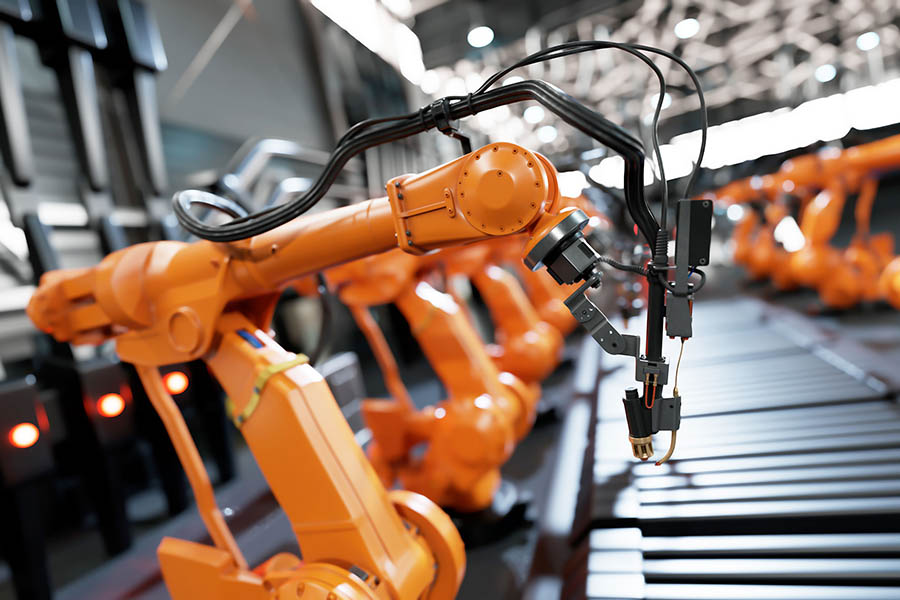








Double-sided PCBs are widely used in a diverse range of applications, particularly in those that require high-performance and reliability.
Consumer electronics: Double-sided PCBs are commonly used in a wide range of consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and home appliances.
Industrial control systems: Double-sided PCBs are used in various industrial control systems, including robotics, automation, and process control.
Medical equipment: Double-sided PCBs are used in various medical devices, including diagnostic equipment, imaging systems, and patient monitoring systems.
Telecommunications: Double-sided PCBs are used in various telecommunications equipment, including routers, switches, and wireless communication systems.
Automotive electronics: Double-sided PCBs are used in automotive electronics, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and navigation systems.
Power supplies: Double-sided PCBs are used in various power supplies, including AC-DC converters, DC-DC converters, and battery chargers.
Aerospace and defense: Double-sided PCBs are used in various aerospace and defense applications, including avionics, radar systems, and satellite communication systems.

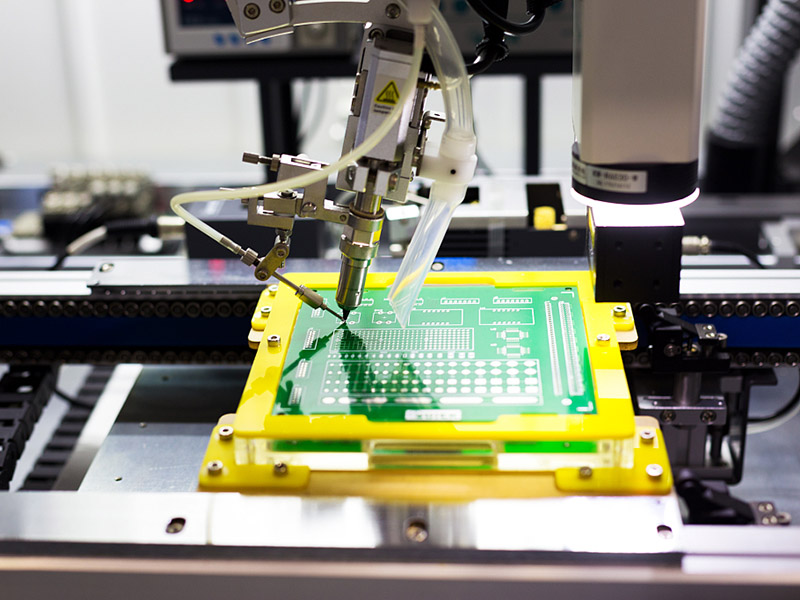

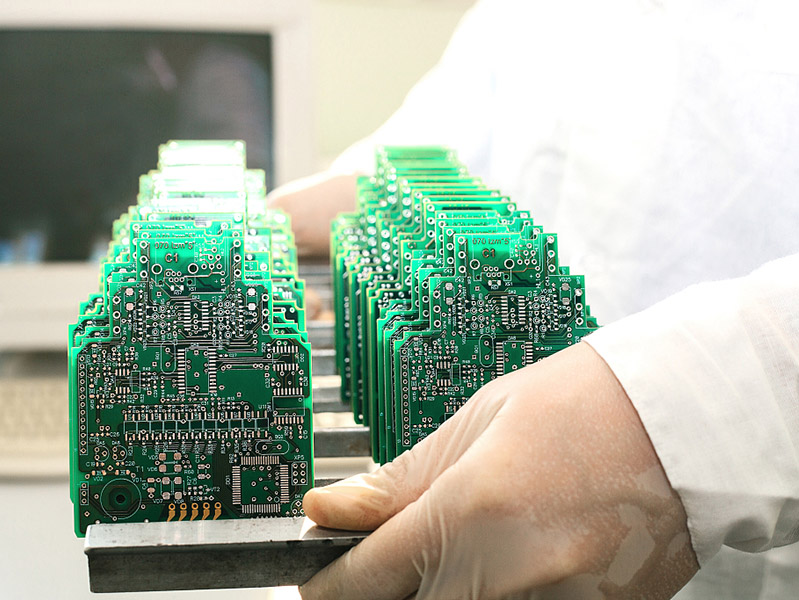
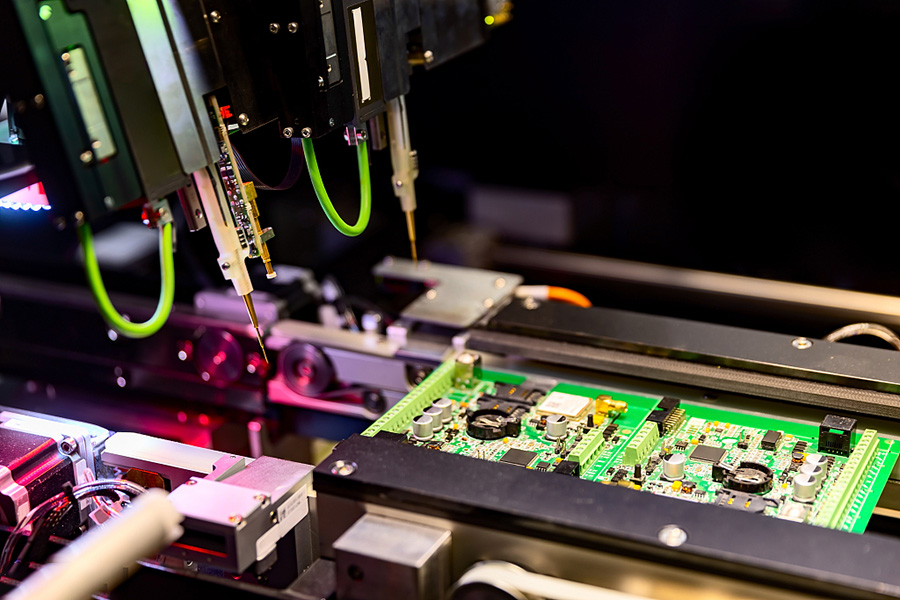
Get a factory directly price quote with 24 hours.
Pls input your email address correctly!
Make sure your name and email is right.