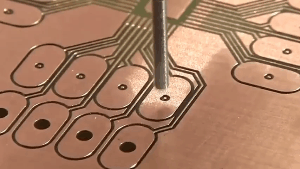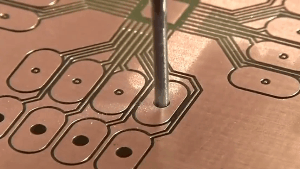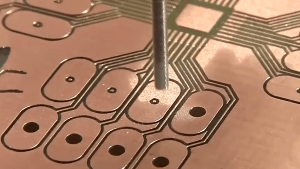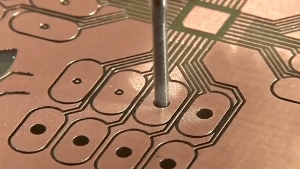
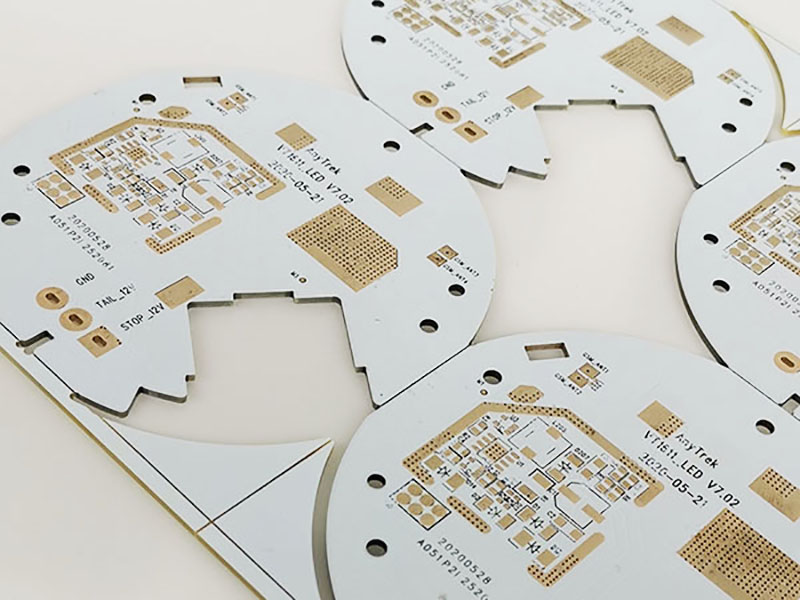
An aluminum PCB (printed circuit board) is a type of circuit board that uses an aluminum substrate as its base material.
The aluminum substrate is typically composed of three layers: a circuit layer (also known as the copper layer), a dielectric layer, and an aluminum layer. The circuit layer is used to create the traces and pads that will be used to connect the components on the board, while the dielectric layer provides electrical insulation between the circuit layer and the aluminum layer.
Excellent thermal conductivity: Aluminum PCBs have a high thermal conductivity, which allows them to dissipate heat effectively. This property makes them ideal for use in high-power applications.
Lightweight and durable: Compared to traditional PCBs, aluminum PCBs are lightweight and durable. They can withstand high levels of stress and strain, making them more resistant to damage from vibrations and shocks.
Good electrical insulation: Aluminum PCBs have a thin layer of dielectric material that provides excellent electrical insulation between the metal layers.
Low cost: Aluminum PCBs are relatively low cost compared to other types of high-performance PCBs.
Easy to assemble: Aluminum PCBs are easy to assemble and can be used with a wide range of surface mount and through-hole components.
Good EMI Shielding: The metal substrate of an aluminum PCB provides good electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, making them suitable for use in applications where EMI is a concern.


Aluminum PCBs have a thermal conductivity coefficient ranging from 10 to 25. They are metal-based copper-clad boards with excellent heat dissipation capabilities.
Typically, a single-sided aluminum PCB is composed of three layers: the circuit layer (copper foil), the insulation layer, and the metal base layer. Some high-end applications may require double-sided aluminum PCBs with a structure consisting of the circuit layer, insulation layer, aluminum base, insulation layer, and circuit layer. A few applications may also require multi-layer aluminum PCBs, which can be produced by bonding a conventional multi-layer board with insulation and an aluminum base.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of aluminum PCBs is determined by the thickness of the copper foil and the insulation layer. The copper foil thickness options include 25μm, 35μm, and 70μm, while the insulation layer options include PP fiberglass cloth (poor thermal conductivity), thermal conductive adhesive (good thermal conductivity), and ceramic powder (excellent thermal conductivity).
Aluminum PCBs have a wide range of applications due to their excellent thermal conductivity and other properties. Some of the common applications of aluminum PCBs include:
LED Lighting: Aluminum PCBs are commonly used in LED lighting due to their high heat dissipation capabilities, which help to increase the lifespan of the LED bulbs.
Power Supplies: Aluminum PCBs are also used in power supply units, such as AC-DC converters, due to their high thermal conductivity and durability.
Automotive Industry: Aluminum PCBs are used in the automotive industry for electronic control units (ECUs), which require high reliability and thermal management.
Audio Equipment: Aluminum PCBs are also used in high-end audio equipment, such as amplifiers and mixing consoles, due to their low thermal resistance and high thermal conductivity.
Aerospace Industry: Aluminum PCBs are used in the aerospace industry for avionics, navigation systems, and satellite communication due to their lightweight and durable nature.
Medical Industry: Aluminum PCBs are used in medical devices, such as MRI machines and pacemakers, due to their biocompatibility and thermal management capabilities.


Get a factory directly price quote with 24 hours.
Pls input your email address correctly!
Make sure your name and email is right.