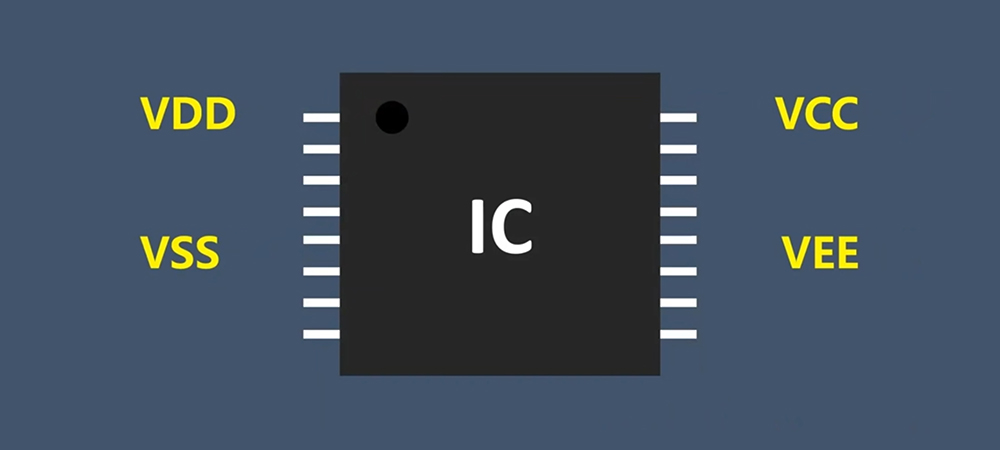
In electronic circuit design, symbols like VCC, VDD, VEE, and VSS are commonly used to represent different power supplies and ground references. Each has specific meanings and applications depending on the type of circuit or device, and understanding these distinctions is essential for circuit designers. This article delves into the definitions of these symbols, their roles in digital and analog circuits, and clears up common misconceptions.
Definitions and Meanings
VCC (Voltage Common Collector)
- Definition: VCC typically denotes the positive voltage supply in bipolar junction transistor (BJT) circuits, connected to the collector. Common values are +5V, +12V, etc.
- Application: It often represents the main positive power source in digital circuits.
VEE (Voltage Common Emitter)
- Definition: VEE is used to denote a negative voltage supply, commonly connected to the emitter in BJT or analog circuits, often at -5V or other negative levels.
- Application: VEE is frequently seen in analog circuits, especially in emitter-coupled logic (ECL).
VDD (Voltage Drain Drain)
- Definition: VDD is the positive supply voltage associated with field-effect transistors (FETs) or CMOS circuits, connected to the drain. Typical values include +3.3V and +5V.
- Application: In CMOS circuits, VDD supplies power to the PMOS transistors.
VSS (Voltage Source Source)
- Definition: VSS generally refers to ground or zero voltage reference, particularly in CMOS circuits, where it’s connected to the source of NMOS transistors.
- Application: In most circuits, VSS serves as the ground line or negative power reference.
Applications in Different Circuits
- Digital Circuits
- VCC: Supplies positive voltage to BJT circuits, often connecting to the collector of NPN transistors.
- VDD: Provides positive voltage to CMOS circuits, specifically to PMOS transistors.
- VSS: Acts as ground or zero potential in CMOS circuits.
- VEE: Supplies negative voltage in ECL circuits.
- Analog Circuits
- VCC: Powers the collector in BJT-based circuits, often the main supply source.
- VDD: Supplies the drain in MOSFET-based amplifier circuits.
- VSS: Serves as the common ground or reference voltage for current return paths.
- VEE: Supplies negative power in circuits requiring dual power supplies.
- MOSFET Devices
- VDD: Refers to the drain voltage in MOSFETs, acting as the main supply voltage.
- VSS: Connects to the source of NMOS transistors, often serving as ground or the lowest potential in the circuit.
- BJT Circuits
- VCC: The primary positive supply voltage, connected to the collector.
- VEE: Provides a negative voltage supply, especially in differential amplifiers.
- CMOS Technology
- VDD: Connected to the source of PMOS transistors, representing the higher voltage level.
- VSS: Serves as ground for NMOS transistors, typically the zero voltage reference.
Common Misunderstandings and Clarifications
Misunderstanding: VCC and VDD Are Interchangeable
Some believe VCC and VDD can be used interchangeably. However, VCC is usually associated with BJT circuits, while VDD refers to MOSFET circuits.
Misunderstanding: VSS Is Always Ground
While VSS is commonly ground, it may represent other voltage levels in certain circuits. Additionally, “ground” (GND) can refer to signal ground, which is not always the same as VSS.
Misunderstanding: VEE Is Always Negative
Although VEE often represents a negative supply, it can be zero or positive depending on the circuit design.
Misunderstanding: Uniform Symbol Usage Across Circuits
The meaning of VCC, VDD, VEE, and VSS varies with circuit types. For example, VCC in BJT circuits and VDD in CMOS circuits both refer to positive supply but differ in context.
Misunderstanding: All ICs Use Standard Symbols
Different ICs may use unique symbols, so engineers should consult datasheets to confirm the meanings of specific symbols.
Misunderstanding: VCC and VDD Are Always Higher Than VEE and VSS
In some designs, VCC or VDD can be negative, and VEE or VSS can be zero or even positive.
Conclusion
An in-depth understanding of VCC, VDD, VEE, and VSS is crucial for effective circuit design. Each symbol has a specific meaning in different types of circuits, and engineers should carefully analyze and apply them based on the device and design requirements. Mastering these distinctions enables more precise circuit design, ensuring stability and performance.
For further insights or professional support in electronic manufacturing, SuperPCBA is here to help. Reach out to us at sales@superpcba.com, and let’s collaborate on bringing your electronic design and manufacturing projects to life.