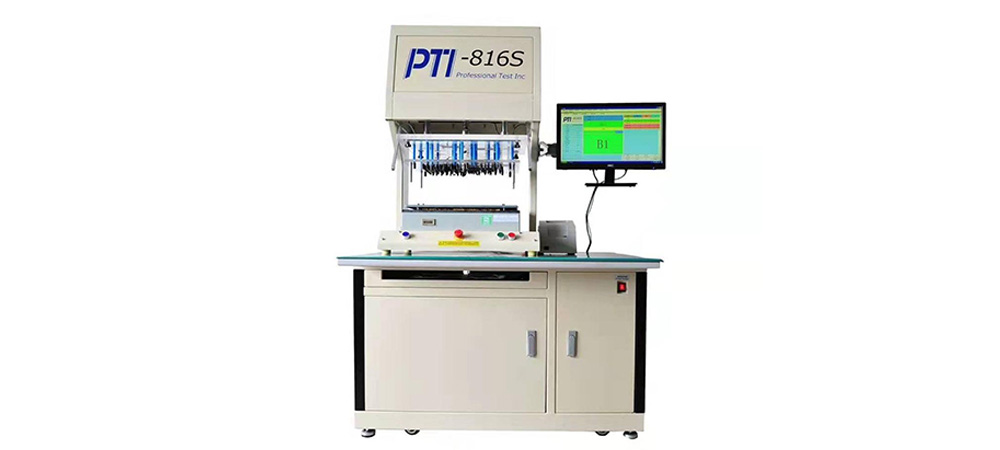
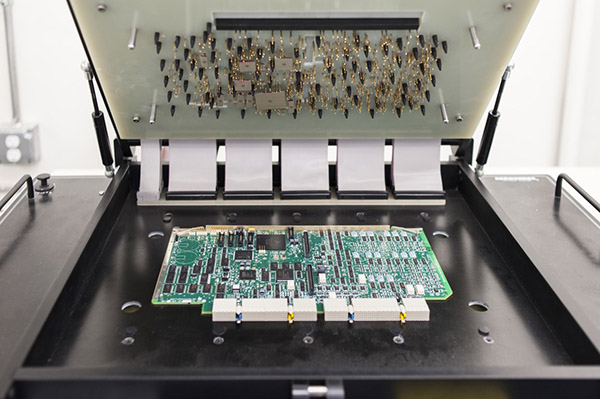
ICT TEST Concept
In-line ICT test is a type of ICT (In-Circuit Test) that is performed during the manufacturing process while the printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is moving along a production line. It is a high-speed test that checks the functionality and performance of the components on the board, as well as verifying the accuracy of the component placement and soldering. In-line ICT test is often used in high-volume production environments as a cost-effective way to detect defects early in the manufacturing process, before the product is completed.
ICT TEST STEPS
Here, I will briefly introduce the content of ICT (In-circuit Test) online test for electronic components and circuit boards. ICT online testing is the first testing station after SMT component placement, which can effectively prevent quality problems in mass production of circuit boards.
1. The first step in ICT station testing is to perform open and short circuit testing on the circuit board. If there are open or short circuits outside the system settings during testing, an error message will be displayed.
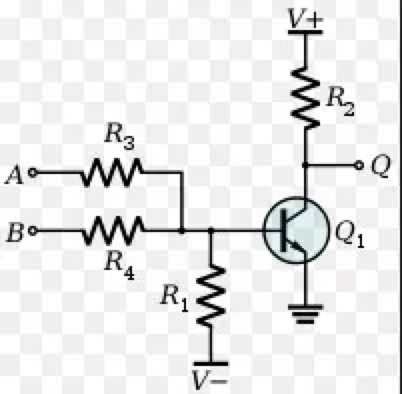
2. If there are no problems with the circuit board, component testing will begin. The testing system will test the independent components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors separately. The main test for diodes and transistors in this step is the forward and reverse conduction test to determine whether they are attached in reverse or incorrectly.
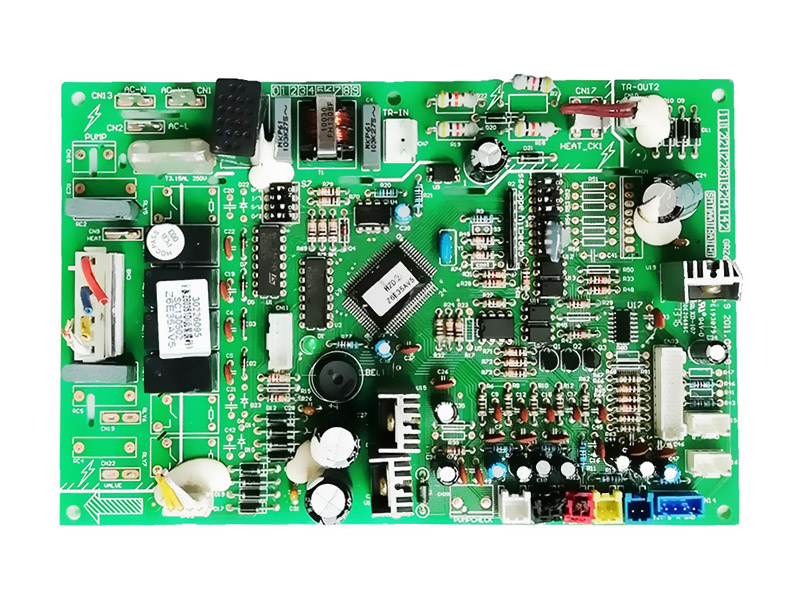
3. Due to the distribution of the circuit board testing pins and the size limitations of the circuit board, not all discrete components can be tested. The next step is modular testing, which is to test a local circuit as a whole to verify its quality.
4. The above tests are all completed without power, called Unpowered test. After passing the unpowered test, the product will be powered up for testing. The testing system will apply power to the product’s power port to allow the product to enter the charged state. This power-on process is controlled by software.
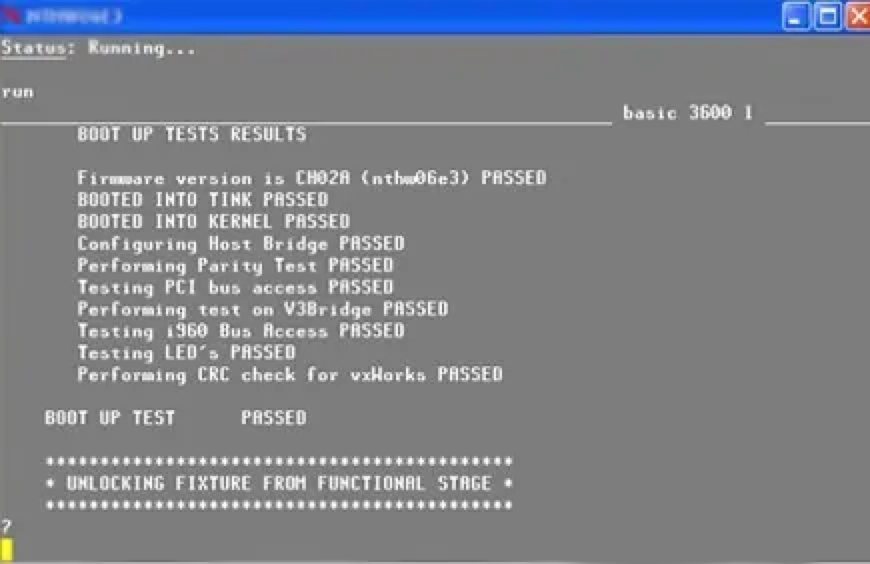
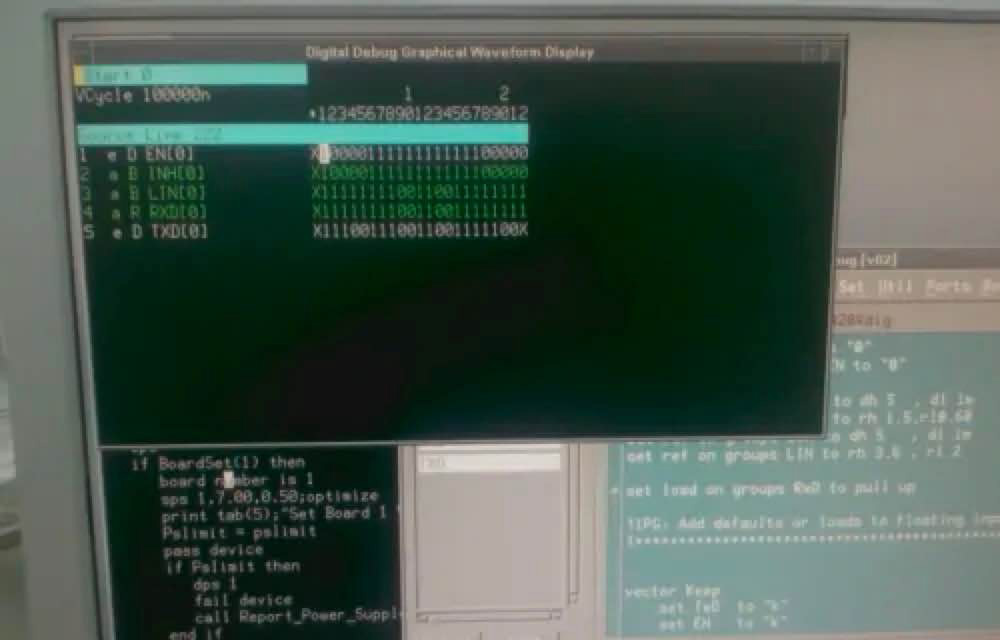
5. After power-up, voltage testing of important voltage points, transistor switching characteristics testing, and chip input and output port high and low voltage level testing will be carried out. The test results shown in the figure are the input and output tests of the CAN bus transceiver working status.
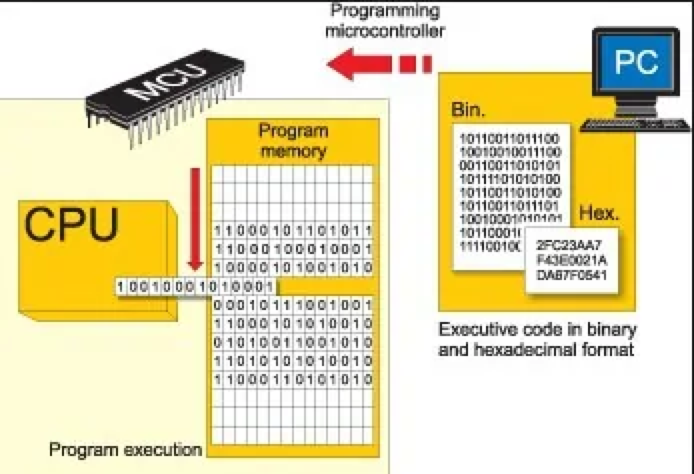
6. If there are no problems with the previous tests, the system will begin the programming process of the product’s main control chip. This process is called programming and is not required for all products and depends on the product’s functionality. After programming is completed, the product’s main control chip will start working and drive the entire product to operate.
6. After the product starts working, some components, such as large capacitor voltage testing and angle sensor testing, need to be tested. These can only be detected when the product is in operation.

7. If there are no problems with the power-on test process, the system will begin to power off the product, then release the electric charge stored in the large capacitor, and finally prompt that the test has passed.
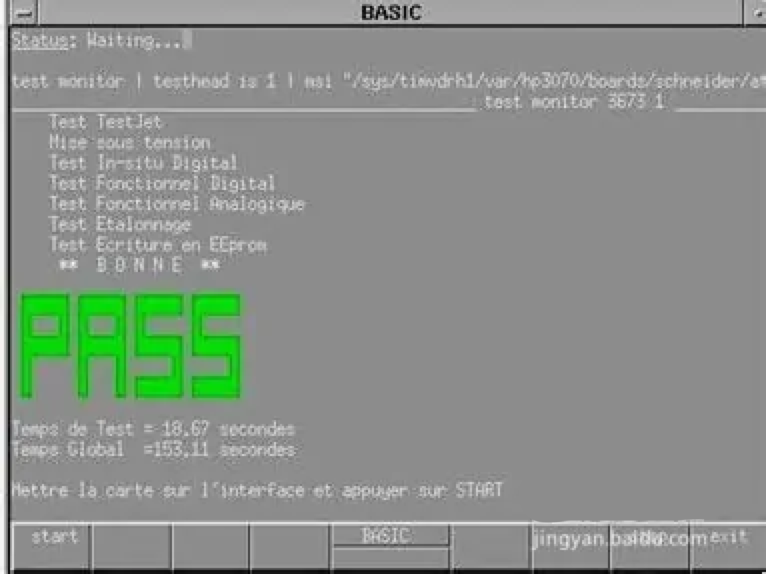
At this point, the entire ICT test is complete. As you can see, the testing process is complex and meticulous. After ICT online testing, functional testing will be conducted with a focus on checking the product’s functionality. Only products that pass multiple tests will be put on the market. Therefore, when using electronic products from reputable manufacturers, there is no need to worry about purchasing untested products.



